Anemia is a condition where the amount of red blood cells and hemoglobin is below normal. Normal levels of hemoglobin for men and women differ, but the specific laboratory references used may tell the exact value. The reference ranges for hemoglobin are 3.5 to 17.5 grams (g) of hemoglobin per deciliter (dL) of blood for men and 12.0 to 15.5 g/dL for women.
Causes of Anemia
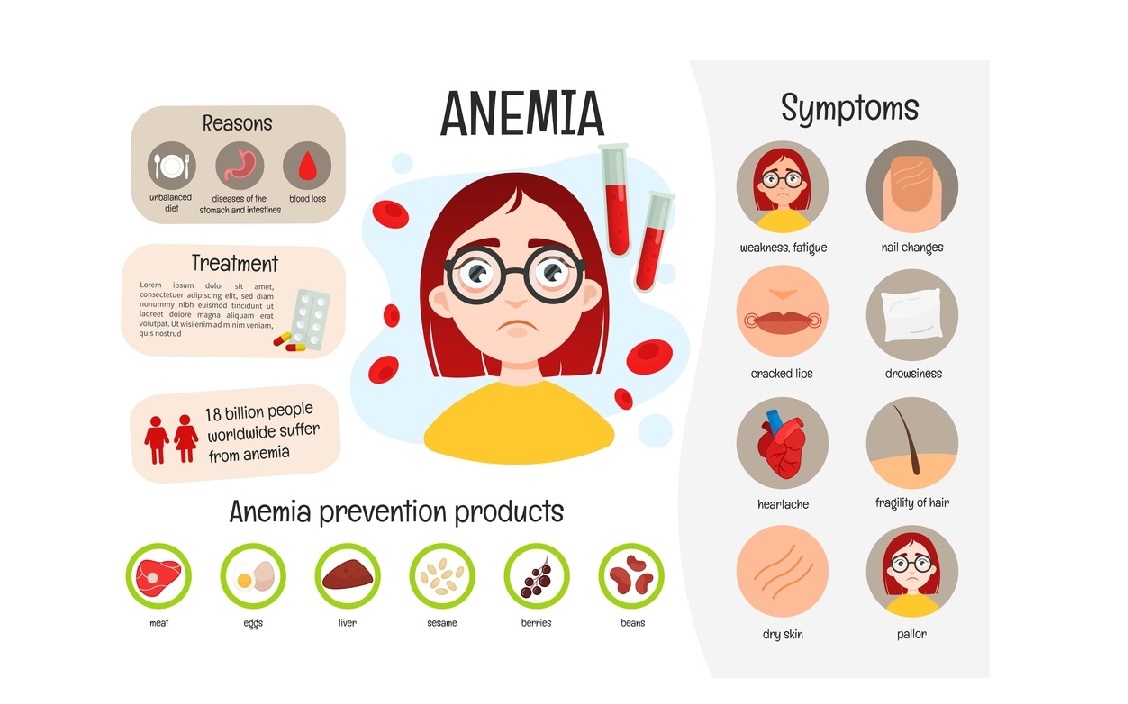
Any process in the body that affects red blood cells negatively can cause this condition. Red blood cells typically survive for 120 days. They are made in the bone marrow, and hence, anemia can occur as a result of:
- Decrease of production of red blood cells caused by issues of the bone marrow.
- Iron deficiency is another common cause of anemia because iron makes up a big part of hemoglobin enabling proper functioning. Excess bleeding is a reason for low iron, as it depletes the body’s iron to compensate for the loss.
- In women, iron deficiency in low amounts usually exists because of menstruation. However, this does not produce any major symptoms.
- Acute blood loss from internal bleeding can lead to anemia as well which needs to be addressed promptly. Dizziness, fatigue, confusion, and shortness of breath are some symptoms.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to it when individuals cannot absorb this vitamin from their food in the digestive system.
- Strict vegetarians may be at risk if supplements aren’t being taken.
- Issues with the bone marrow can also lead to it, as the bone marrow produces red blood cells. Bone marrow damage can also arise from chemotherapy.
- Sometimes antibodies may cling to red blood cells, causing anemia.
- Anemia can be genetic, and these issues shorten the lifespan of red blood cells or impair hemoglobin production.
What are the complications associated with anemia?
Hemoglobin delivers oxygen to all parts of our body for consumption and carries carbon dioxide back to exhale it out of our bodies. If hemoglobin levels are very low, it may lead to hypoxia or very low oxygen levels in the body, which can lead to a lot of complications.
Symptoms of anemia:
Sometimes, anemia doesn’t result in symptoms. But most commonly seen ones include:
- Tired
- Fatigue
- Pale skin
- Heart racing
- Shortness of breath
- Hair loss
- Weakness
- Worsening of existing heart issues
If anemia is slowly progressing, the body may get used to low oxygen levels and symptoms may not be felt. But if acute, then symptoms may be felt pretty quickly.
Diagnosis of Anemia
The presence of anemia is told usually using a CBC test or a complete blood count test. This is often ordered as part of any regular health checkup by a physician. Abnormalities with the blood can easily suggest anemia diagnosis or other issues with blood.
What is a complete blood cell (CBC) count?
For more detailed information about complete blood cell (CBC) Click here
Six component measurements are taken in this test:
- Red blood cell (RBC) count
- Hematocrit
- Hemoglobin
- White blood cell (WBC) count
- Differential blood count (the “diff”)
- Platelet count
The first three readings are the most useful to detect anemia.
Treatment of anemia
The different kinds of anemia that can be caused by the body warrant different treatment:
- Anemia from blood loss from any part of the body should focus on healing the part of the body that shows such loss of blood. Surgery is often needed to remove tumors, or large ulcers causing these issues.
- Iron supplements or B12 injections may be needed to solve iron deficiency issues and prevent anemia. In severe cases, blood transfusions may be needed to make up for losses.
- In patients where anemia is a result of bone marrow issues, the best way to stimulate bone marrow red cell production is to administer Procrit and Epogen. This is even useful in case of kidney failure.
- If a medication is thought to be the cause of anemia, it should be discontinued after consulting your doctor.