
Rapid Antibody Testing is a blood test that can indicate presence or absence of antibodies against the virus in the tested sample. The results can be obtained on the spot within 10-30 minutes. Antibody tests help in determining whether someone suspected of COVID-19 has developed immunity or not. However, it doesn’t assess the quantitative presence of antibodies and the probability of future infections.
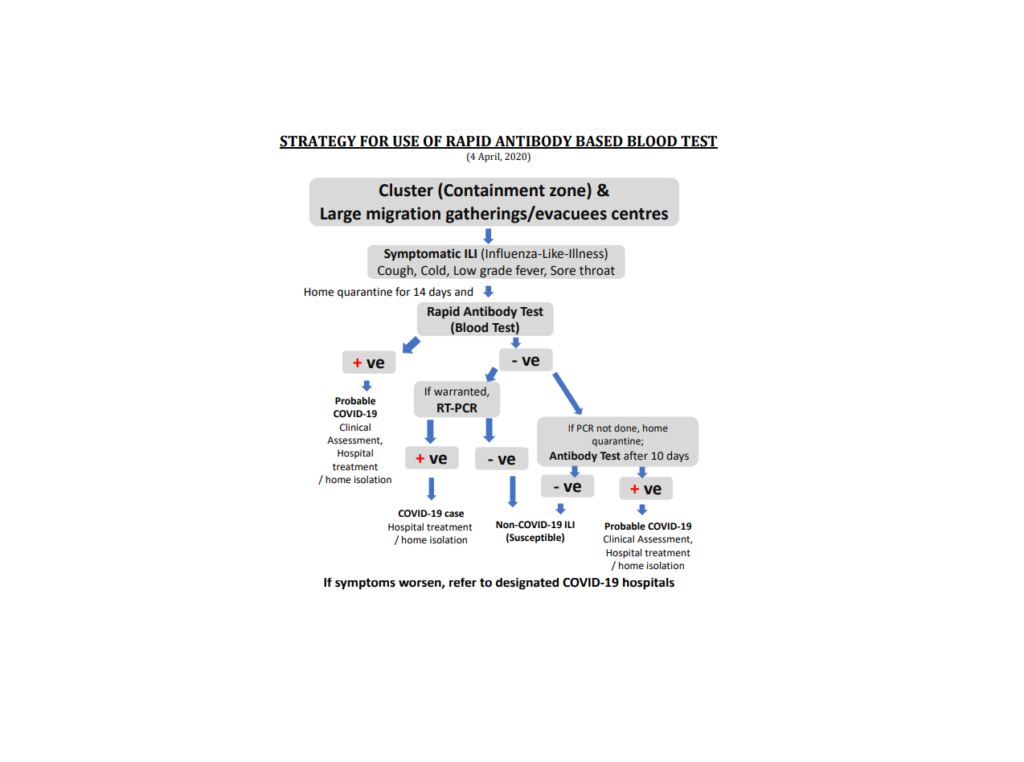
In the current scenario of COVID-19 pandemic, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has authorized rapid antibody testing for all symptomatic individuals in hotspots in the country. A Positive result means presence of antibody against COVID-19 virus in vivo and indicates present or past infection to COVID-19. Presence of IgM antibody indicates present or recent infection and presence of IgG antibody indicates past infection. As per ICMR guidelines, patients testing positive must be admitted in hospital for further monitoring and treatment and contact tracing has to be started immediately. A Negative result in a symptomatic patient means absence of antibody against COVID-19 virus in vivo. It indicates that the patient either does not have the infection or he/she is in the window period when the antibody is still to be developed. In such cases, WHO mandated Real Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) test will be conducted to ascertain that the individual is not infected.
In order to safely return to normalcy, limit the economic damage, revoke the trade and movement restrictions, it is important to assess the immunity and risk to COVID-19. This becomes particularly important for doctors and nurses, who are the first line of defence against the pandemic, to know whether they have antibodies. However, it is important to note, antibody detection is NOT used for DIAGNOSIS as per current guidelines.
Advantages of Antibody Testing over RT-PCR
- Antibody based tests are easy to perform, are rapid and definitely cost effective. The exact price of antibody tests are yet to be capped by ICMR, however, they will be relatively cheaper than RT-PCR.
- The chances of false-negatives are lower with antibody testing as antigens and antibodies are considerably more stable than RNA, which makes them less susceptible to spoliation during transport and storage. Antigens and antibodies are more uniformly available in sputum and blood samples, which improve the testing accuracy.
- Ability to detect past infections as antibodies are long-lasting and can persist in the bloodstream for many years after infection and thus help in Retrospective Detection.
- Contact tracing could become easier as the type of antibody and its relative levels could also be used to indicate the stage of infection and estimate time since exposure.